

The raceway of a gearbox bearing can be inspected for signs of wear and damage by visually examining the surface for any discoloration, pitting, or scoring. Additionally, running a finger along the raceway can help detect any rough spots or irregularities that may indicate wear. Using a magnifying glass or a borescope can provide a closer look at the raceway surface to identify any signs of damage that may not be visible to the naked eye.
Common methods used to measure the surface roughness of a gearbox bearing raceway include profilometers, surface roughness testers, and optical interferometry. These tools can provide quantitative data on the roughness of the raceway surface, which can help determine the level of wear and potential for future damage. By measuring the surface roughness, maintenance professionals can assess the condition of the raceway and plan for necessary repairs or replacements.
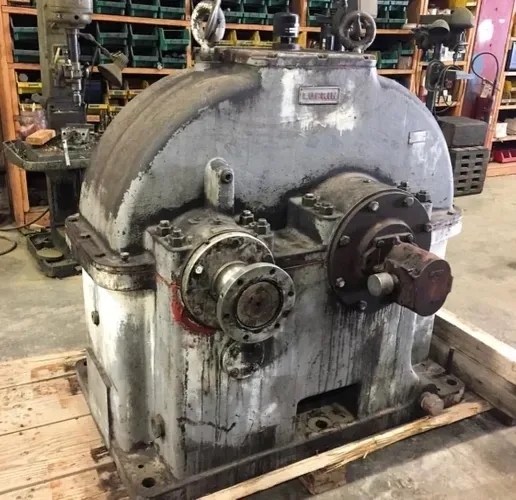
Expert Insights Into The Equipment Behind Industrial Gearbox Repair
Episode: 1132 In which balloons deliver the mail during the Siege of Paris. Today, the very first airmail service is used to break a siege.
Posted by on 2024-03-11
Episode: 1131 John Hunter: idiosyncratic medical pioneer. Today, the history of medicine provides a strange hero.
Posted by on 2024-03-10
Episode: 1129 In which Alphonse Penaud invents the model airplane. Today, a very young man teaches us to fly, after all.
Posted by on 2024-03-09
The new fiscal year begins in July and the city is anticipating a budgetary gap of about $160 million.
Posted by on 2024-03-08
Key indicators of fatigue and spalling in a gearbox bearing raceway include flaking, cracking, and peeling of the surface material. These signs are often accompanied by increased noise, vibration, and temperature in the gearbox. By monitoring these indicators during regular inspections, maintenance personnel can identify potential issues early on and take corrective actions to prevent further damage to the raceway and the gearbox as a whole.

The lubrication condition of a gearbox bearing raceway can be assessed during inspection by checking the level and quality of the lubricant present. Signs of inadequate lubrication include dry spots, discoloration, and debris buildup on the raceway surface. Additionally, analyzing the viscosity and contamination level of the lubricant can provide insights into the effectiveness of the lubrication system and help prevent premature wear and damage to the raceway.
Recommended inspection intervals for gearbox bearing raceways vary depending on the operating conditions of the gearbox. In general, gearbox bearing raceways should be inspected at least annually or more frequently if the gearbox operates under high loads, speeds, or temperatures. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues early on and prevent costly downtime and repairs in the future.
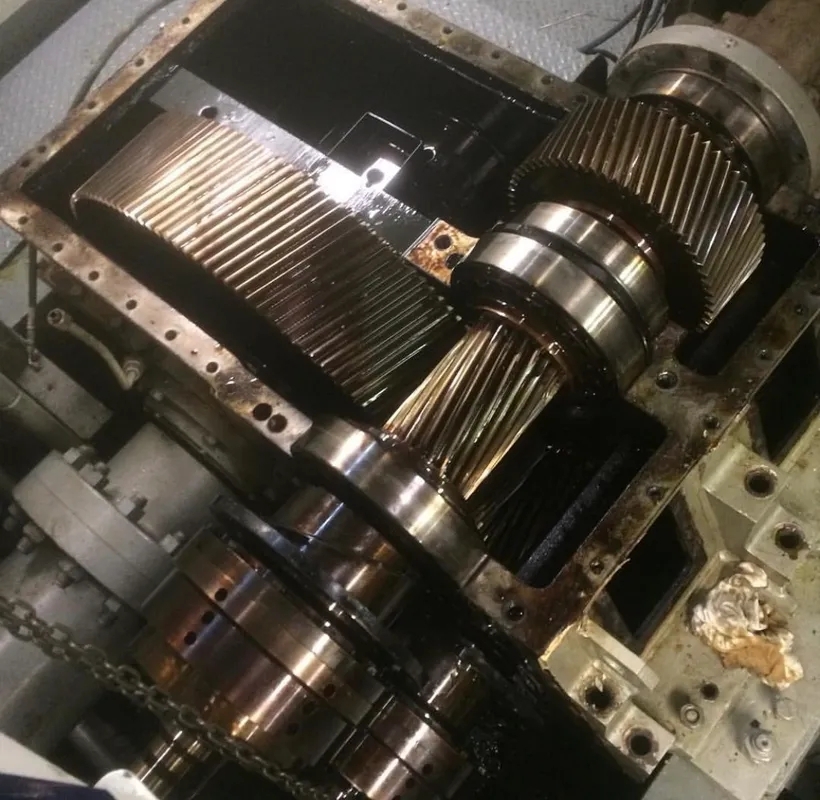
Neglecting regular inspection and maintenance of gearbox bearing raceways can lead to a range of consequences, including increased wear, reduced efficiency, and potential catastrophic failure of the gearbox. Without proper maintenance, issues such as fatigue, spalling, and inadequate lubrication can go unnoticed and escalate over time, resulting in costly repairs, downtime, and safety risks for personnel operating the equipment.
Recommended maintenance procedures for gearbox housings include regular inspections for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks. It is important to check the housing for any cracks, dents, or other damage that could compromise its integrity. Additionally, lubrication of the gearbox housing is essential to ensure smooth operation and prevent overheating. Cleaning the housing regularly to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants is also recommended to prevent premature wear and tear. Proper storage of the gearbox housing when not in use can help prolong its lifespan and prevent damage. Overall, following a comprehensive maintenance schedule and addressing any issues promptly can help ensure the longevity and efficiency of gearbox housings.
In order to reduce gearbox friction, various measures can be implemented. One approach is to use high-quality lubricants that have low viscosity and high thermal stability. Additionally, optimizing the gear tooth profile and surface finish can help minimize frictional losses. Utilizing advanced materials such as carbon fiber or ceramic coatings can also reduce friction within the gearbox. Proper alignment and clearance settings between gears can further decrease friction. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the gearbox components can ensure smooth operation and minimize friction over time. Overall, a combination of lubrication, design optimization, material selection, and maintenance practices can effectively reduce gearbox friction.
The performance of a gearbox can indeed be influenced by external factors such as temperature. Fluctuations in temperature can impact the viscosity of the lubricating oil within the gearbox, affecting its ability to properly lubricate the gears and bearings. Extreme temperatures can also cause thermal expansion or contraction of gearbox components, leading to misalignment or increased friction. Additionally, temperature variations can alter the material properties of gearbox components, potentially leading to premature wear or failure. Therefore, it is crucial for gearbox manufacturers to consider the effects of temperature on performance and design their products accordingly to ensure optimal operation in diverse environmental conditions.
Preventing gearbox corrosion in humid environments can be achieved by implementing various protective measures. One effective method is to apply a corrosion-resistant coating on the gearbox components, such as zinc plating or powder coating. Additionally, using desiccants or dehumidifiers in the surrounding area can help reduce moisture levels and prevent corrosion. Regularly inspecting the gearbox for any signs of corrosion and promptly addressing any issues can also help prevent further damage. Proper ventilation and ensuring proper drainage around the gearbox can also help mitigate the effects of humidity. Overall, a combination of protective coatings, moisture control, regular maintenance, and proper ventilation can help prevent gearbox corrosion in humid environments.
The maintenance schedule for gearbox seals should include regular inspections, typically every 6 months or as recommended by the manufacturer. During these inspections, it is important to check for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks in the seals. This can involve checking the seal material for cracks, tears, or deterioration, as well as ensuring proper alignment and tightness of the seals. Additionally, lubrication of the seals may be necessary to prevent friction and prolong their lifespan. Any issues found during inspections should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage to the gearbox and ensure optimal performance. Following a consistent maintenance schedule for gearbox seals can help prevent costly repairs and downtime in the long run.