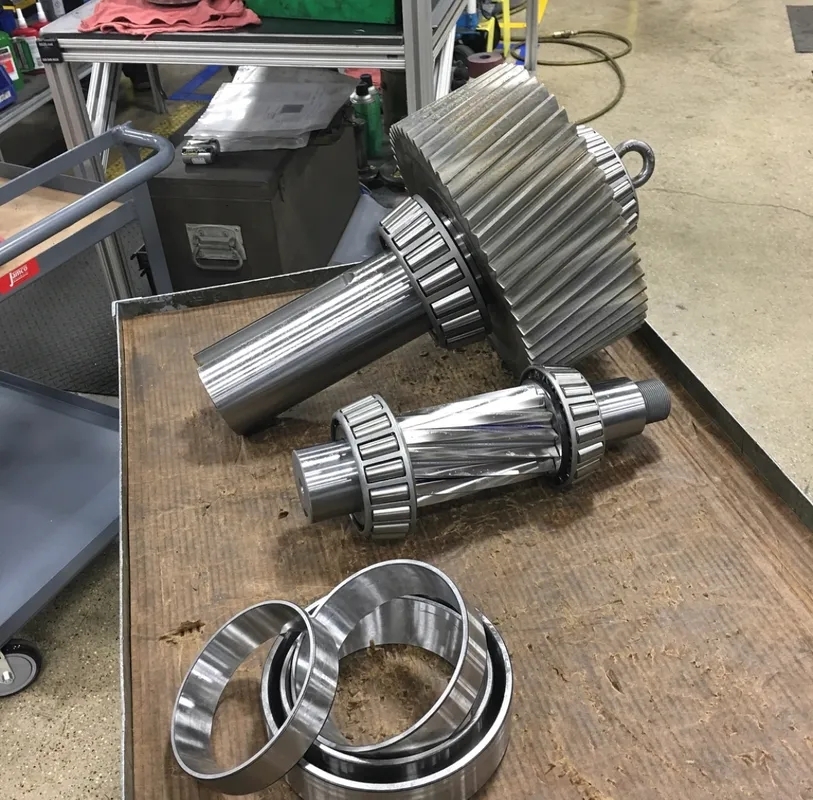


When testing compatibility for gearbox components, key material properties to consider include strength, toughness, fatigue resistance, and thermal conductivity. Strength is crucial to ensure the components can withstand the stresses and loads placed on them during operation. Toughness is important to prevent premature failure due to impact or shock loading. Fatigue resistance is essential to ensure the components can withstand repeated cycles of loading without developing cracks or fractures. Thermal conductivity is important to ensure efficient heat dissipation and prevent overheating of the gearbox components.
The coefficient of thermal expansion plays a significant role in the compatibility of gearbox component materials. Components made from materials with different coefficients of thermal expansion can experience differential expansion or contraction when exposed to temperature variations. This can lead to stress concentrations, dimensional changes, and ultimately, component failure. Therefore, it is essential to select materials with similar coefficients of thermal expansion to ensure compatibility and prevent issues related to thermal cycling.
Expert Insights Into The Equipment Behind Industrial Gearbox Repair
Houston Matters goes behind the scenes of the University of Houston-Downtown's new digital concert series.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Don McLaughlin, who called on the investigation, said acting police chief Mariano Pargas failed as a leader on the day of the mass shooting.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Rivera last week was charged with capital murder and police escalated their searching efforts for the suspect.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
On Tuesday's show: We discuss a number of environmental stories across the state. And we consider how to deal with seasonal allergies as we near the official start of spring.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Episode: 2851 The Lake Breeze Fan: Unplanned Obsolescence. Today, invention and obsolescence.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Hardness is a critical factor in determining the compatibility of materials for gearbox components. Components with inadequate hardness may wear prematurely, leading to reduced lifespan and potential failure. On the other hand, components that are too hard may be brittle and prone to cracking under load. Therefore, selecting materials with the appropriate hardness is essential to ensure the longevity and reliability of gearbox components.
Corrosion resistance is another important consideration when selecting materials for gearbox components. Gearboxes are often exposed to harsh operating environments that can lead to corrosion and degradation of materials over time. Choosing materials with high corrosion resistance can help prevent rust, pitting, and other forms of corrosion that can compromise the performance and integrity of gearbox components. Stainless steels, for example, are commonly used in gearbox applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance properties.
Wear resistance is crucial in determining the compatibility of gearbox component materials. Gearboxes experience significant wear and friction during operation, which can lead to material loss, surface damage, and reduced performance. Selecting materials with high wear resistance, such as hardened steels or ceramics, can help minimize wear and prolong the lifespan of gearbox components. Proper material selection based on wear resistance can ensure the durability and efficiency of the gearbox system.
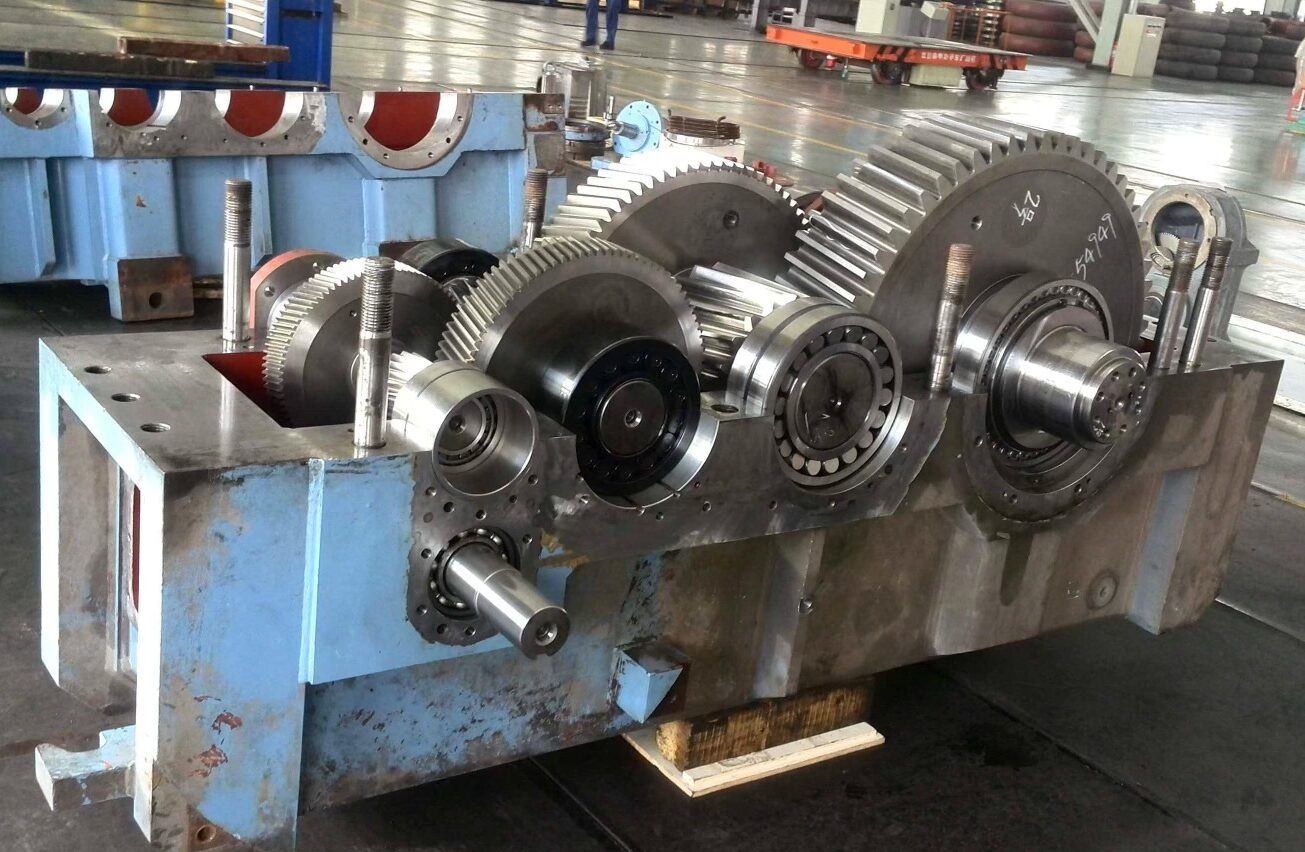

Lubrication compatibility is a key factor that influences the choice of materials for gearbox components. Some materials may have adverse reactions to certain lubricants, leading to degradation, swelling, or loss of mechanical properties. It is essential to select materials that are compatible with the lubricants used in the gearbox system to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Materials that are resistant to lubricant breakdown and offer good lubricity can help reduce friction, wear, and heat generation within the gearbox components.
Common testing methods used to evaluate the compatibility of materials for gearbox components include material analysis, mechanical testing, thermal testing, and accelerated aging tests. Material analysis techniques such as spectroscopy and microscopy can provide insights into the composition, structure, and properties of materials. Mechanical testing methods like tensile testing, hardness testing, and impact testing can assess the mechanical strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance of materials. Thermal testing can evaluate the thermal conductivity, expansion, and stability of materials under different temperature conditions. Accelerated aging tests can simulate the long-term performance and durability of materials in accelerated timeframes to predict their behavior in real-world applications. By utilizing these testing methods, engineers can ensure the compatibility and reliability of materials for gearbox components.
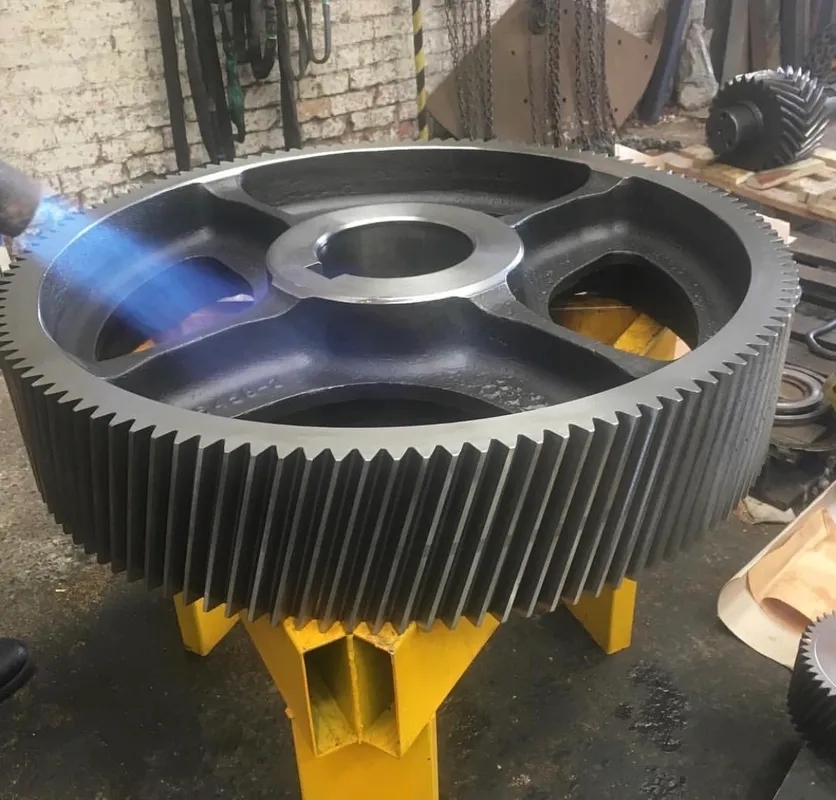

After assembly, it is crucial to follow best practices for gearbox inspection to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The first step is to visually inspect the gearbox for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or misalignments. Next, the technician should check the gear teeth for wear, pitting, or chipping, as well as the bearings for any signs of overheating or excessive play. It is also important to verify that all fasteners are properly tightened and that the lubrication levels are adequate. Additionally, conducting a thorough run-in procedure to ensure proper meshing of gears and smooth operation is recommended. Finally, performing vibration analysis and noise level testing can help identify any potential issues before they escalate. By following these best practices, technicians can catch any problems early on and prevent costly repairs or downtime.
When interpreting gearbox temperature readings, it is important to consider various factors such as the operating conditions, lubrication system efficiency, ambient temperature, and the type of gearbox being used. High gearbox temperatures could indicate issues such as inadequate lubrication, overloading, misalignment, or worn-out components. On the other hand, low temperatures may suggest insufficient load or poor heat dissipation. It is crucial to monitor temperature trends over time and compare them to manufacturer recommendations to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential damage. Regular maintenance and inspection can help identify and address any issues related to gearbox temperature readings.
In pharmaceutical applications, there are specific gearbox maintenance requirements that must be adhered to in order to ensure optimal performance and compliance with industry regulations. These requirements may include regular inspections, lubrication checks, and temperature monitoring to prevent contamination and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, proper documentation of maintenance activities and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are essential in pharmaceutical settings to guarantee the safety and efficacy of products. It is crucial for pharmaceutical companies to work closely with gearbox manufacturers and maintenance professionals to develop a comprehensive maintenance plan tailored to their specific needs and requirements. Failure to properly maintain gearboxes in pharmaceutical applications can result in costly downtime, product recalls, and potential regulatory issues.
Gearbox noise analysis can be a complex process that requires specialized techniques to accurately diagnose and address issues. Some of the key methods used in gearbox noise analysis include vibration analysis, acoustic testing, modal analysis, and frequency spectrum analysis. These techniques allow engineers to identify specific sources of noise within the gearbox, such as gear meshing, bearing defects, or lubrication issues. By using advanced tools such as accelerometers, microphones, and spectrum analyzers, experts can pinpoint the root cause of the noise and develop targeted solutions to reduce or eliminate it. Additionally, computer-aided design (CAD) software can be used to simulate gearbox operation and predict potential noise issues before they occur. Overall, a combination of these specialized techniques is essential for effective gearbox noise analysis and troubleshooting.