

A torque limiter functions as a gearbox overload protection device by sensing when the torque exceeds a predetermined limit and disengaging the drivetrain to prevent damage. This is typically achieved through the use of friction plates or balls that slip when the torque reaches a certain threshold, allowing the gearbox to continue rotating without transmitting excessive force. By limiting the torque, the torque limiter helps protect the gearbox from overload conditions that could lead to costly repairs or downtime.
The advantages of using a shear pin as a gearbox overload protection mechanism lie in its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. A shear pin is designed to break when the torque exceeds a certain level, effectively disconnecting the drivetrain and preventing damage to the gearbox. This straightforward design makes shear pins easy to replace and maintain, reducing downtime and repair costs. Additionally, shear pins are reliable and can be customized to break at specific torque levels, providing tailored protection for different gearbox applications.
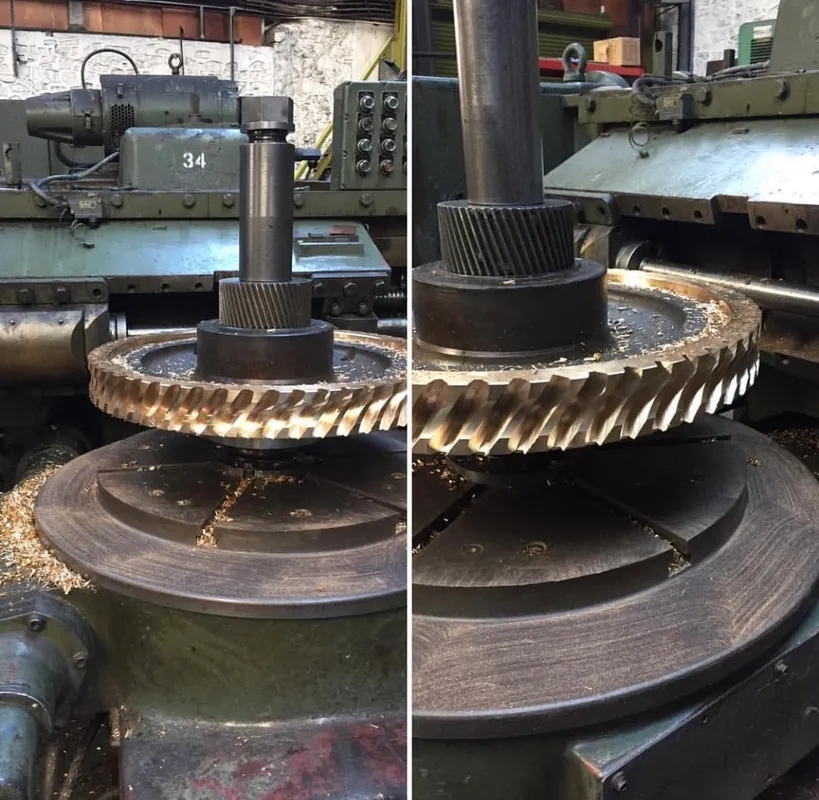
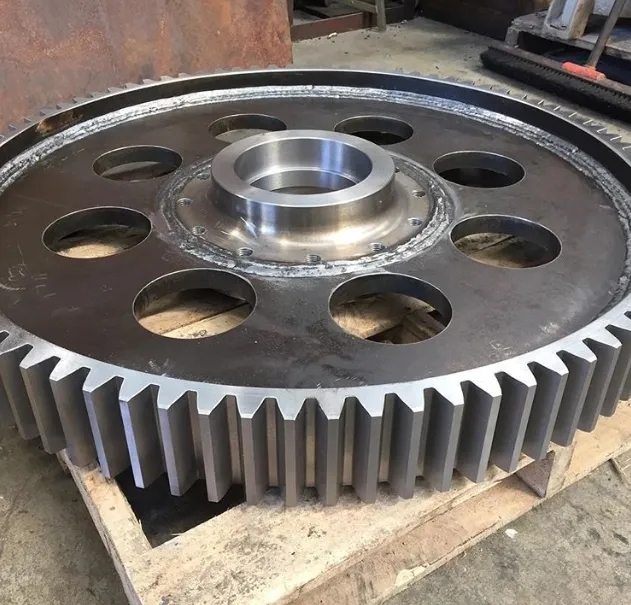
Expert Insights Into The Equipment Behind Industrial Gearbox Repair
Seven people have died in officer-involved shootings just this month in the Houston area, including in Galveston, Conroe and Montgomery. Each of the men who died was holding a gun at the time that they were shot, and one was brandishing a knife, according to the Houston Police Department.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Houston Matters goes behind the scenes of the University of Houston-Downtown's new digital concert series.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Don McLaughlin, who called on the investigation, said acting police chief Mariano Pargas failed as a leader on the day of the mass shooting.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Rivera last week was charged with capital murder and police escalated their searching efforts for the suspect.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
A slip clutch can be adjusted to provide different levels of overload protection for a gearbox by changing the amount of pressure applied to the clutch plates. By adjusting the spring tension or friction material, the slip clutch can be set to slip at varying torque levels, allowing for customized protection based on the specific requirements of the gearbox. This flexibility makes slip clutches a versatile option for applications where varying levels of overload protection are needed.

A centrifugal clutch provides automatic overload protection for a gearbox by using centrifugal force to engage and disengage the drivetrain based on the rotational speed of the input shaft. When the speed exceeds a certain threshold, the centrifugal force causes the clutch to engage, transmitting power to the gearbox. However, if the speed drops suddenly or the load increases beyond a safe limit, the clutch disengages, preventing damage to the gearbox. This automatic protection mechanism helps ensure the longevity and reliability of the gearbox in various operating conditions.
Common signs that indicate a gearbox overload protection device needs to be replaced or repaired include unusual noises, such as grinding or clunking sounds, erratic behavior, such as slipping or jerking movements, and decreased performance, such as reduced power output or efficiency. Additionally, visible damage to the overload protection device, such as worn or broken components, can indicate that it is no longer functioning properly and needs to be inspected or replaced to prevent further damage to the gearbox.
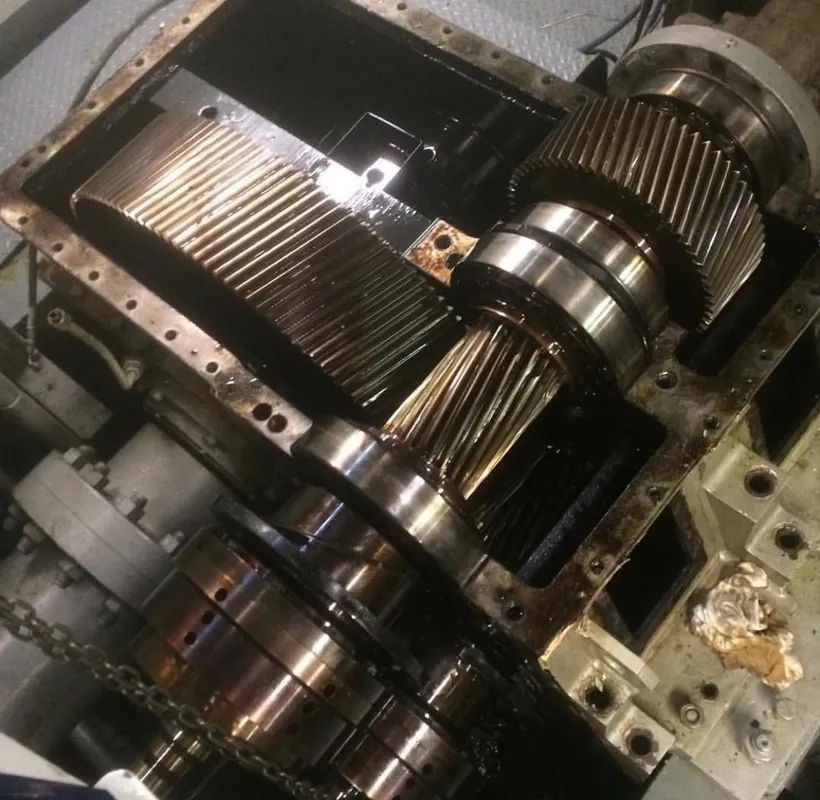
There are different types of overload protection devices available for specific gearbox applications, such as industrial vs automotive. For industrial gearboxes, heavy-duty torque limiters or shear pins may be used to withstand high torque loads and provide robust protection against overloads. In contrast, automotive gearboxes may utilize slip clutches or centrifugal clutches for automatic protection during varying driving conditions. The choice of overload protection device depends on the specific requirements and operating conditions of the gearbox in question.
A gearbox overload protection device can help prevent costly damage to equipment and machinery by detecting and mitigating overload conditions before they cause significant harm. By limiting the torque, disconnecting the drivetrain, or automatically adjusting the engagement based on speed, these devices safeguard the gearbox from excessive forces that could lead to premature wear, breakdowns, or catastrophic failures. By investing in reliable overload protection mechanisms, operators can ensure the longevity and efficiency of their gearboxes, ultimately saving time and money on repairs and replacements.

Gearbox thermal expansion is primarily influenced by factors such as operating temperature, material composition, lubrication type, and design geometry. The temperature at which the gearbox operates plays a significant role in determining the extent of thermal expansion experienced. Additionally, the specific materials used in the construction of the gearbox, such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials, can impact how much thermal expansion occurs. The type of lubrication used within the gearbox can also affect thermal expansion, as different lubricants have varying thermal properties. Furthermore, the design geometry of the gearbox, including the size and shape of components, can contribute to thermal expansion by influencing how heat is distributed throughout the system. Overall, a combination of these factors can lead to thermal expansion in gearboxes during operation.
In dusty environments, it is crucial to perform regular gearbox maintenance tasks to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Some specific tasks include cleaning the gearbox housing, inspecting seals for any signs of wear or damage, checking for any buildup of dust or debris on gears and bearings, and lubricating moving parts to prevent friction and wear. It is also important to regularly replace filters and breathers to prevent dust from entering the gearbox and causing damage. Additionally, using dust-resistant seals and covers can help protect the gearbox from the harmful effects of dust and debris. By following these maintenance tasks, the gearbox can continue to operate efficiently in dusty environments.
Various types of gear tooth damage can indicate gearbox problems, such as pitting, spalling, scoring, and wear. Pitting occurs when small craters or pits form on the gear teeth due to excessive loads or inadequate lubrication. Spalling is characterized by the flaking or chipping of the gear tooth surface, often caused by fatigue or material defects. Scoring refers to the presence of scratches or grooves on the gear teeth, typically caused by abrasive contaminants in the lubricant. Wear, on the other hand, occurs when the gear teeth gradually lose material over time due to friction and load. Identifying these types of gear tooth damage is crucial in diagnosing gearbox issues and preventing further damage to the system.
In food-grade applications, there are specific gearbox maintenance requirements that must be adhered to in order to ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards. These requirements typically include regular inspections, lubrication checks, and cleaning procedures to prevent contamination and ensure the gearbox operates efficiently. It is important to use food-grade lubricants and materials that are safe for use in food processing environments. Additionally, proper documentation and record-keeping of maintenance activities are essential for traceability and audit purposes. Failure to follow these maintenance requirements can result in product contamination, equipment failure, and potential regulatory violations. Therefore, it is crucial for operators in food-grade applications to prioritize gearbox maintenance as part of their overall food safety program.
When troubleshooting gearbox lubrication pump problems, it is important to first check for any leaks, blockages, or malfunctions in the pump system. Inspect the pump for any signs of wear and tear, such as damaged seals or bearings. Ensure that the pump is properly lubricated and that the oil levels are within the recommended range. Test the pump's pressure and flow rate to determine if it is functioning correctly. Additionally, check the pump's electrical connections and controls to ensure they are working properly. If the issue persists, it may be necessary to consult a professional technician for further diagnosis and repair.
When determining the appropriate gearbox lubricant type, it is important to consider factors such as viscosity, additives, and base oil type. Viscosity is crucial as it affects the lubricant's ability to flow and provide adequate protection to the gearbox components. Additives, such as anti-wear agents and corrosion inhibitors, can enhance the lubricant's performance and extend the gearbox's lifespan. The base oil type, whether mineral, synthetic, or semi-synthetic, also plays a significant role in determining the lubricant's compatibility with the gearbox materials and operating conditions. Conducting a thorough analysis of the gearbox specifications, manufacturer recommendations, and operating environment can help in selecting the most suitable lubricant type for optimal performance and longevity.