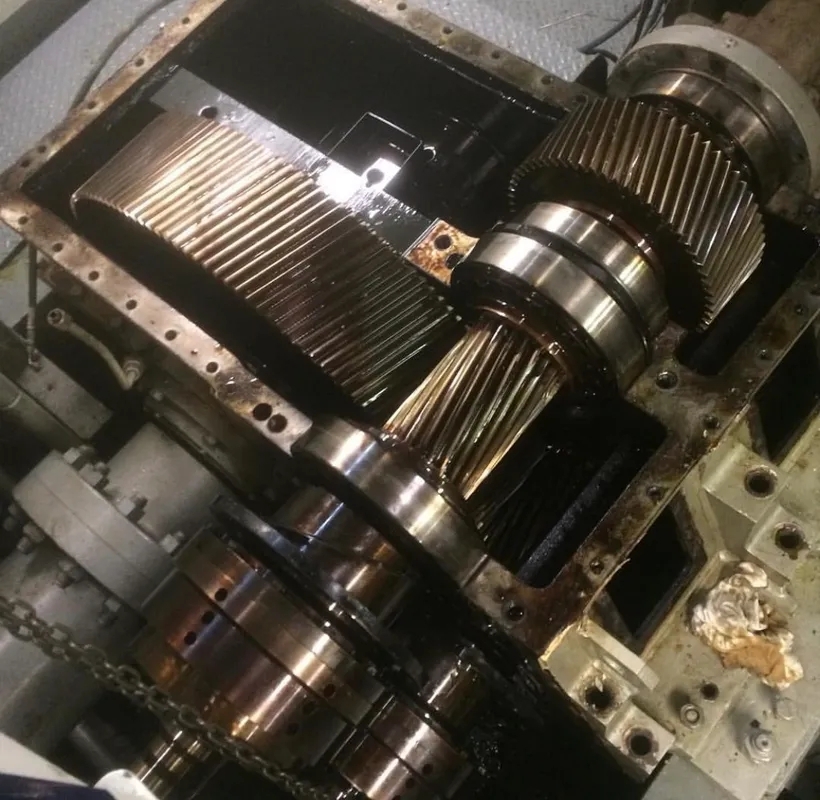

Gearbox housing cracks can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive vibration, overloading, poor maintenance, material defects, and manufacturing flaws. These cracks can compromise the structural integrity of the gearbox housing, leading to potential leaks, failures, and safety hazards if not addressed promptly.
Visual inspection is a crucial method for detecting cracks in gearbox housings. By closely examining the surface of the housing, inspectors can look for visible signs of cracking, such as hairline fractures, discoloration, or irregularities in the metal. This method allows for quick identification of potential issues that may require further testing or repairs.
On Wednesday's show: We discuss the latest developments in politics, including whether runoffs ever have dramatically different results. Then we consider if we are ready for the next major public health emergency.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
Episode: 2998 Test Tube Evolution. Today, evolution in a test tube.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
Dr. Talat Jehan Khan, a pediatrician for Texas Children's Hospital, was stabbed to death Oct. 28 in an outdoor common area at Alys Luxury Living in Conroe. The man accused of killing her is jailed and faces a murder charge.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
The university is partnering with the Ibn Sina Foundation and the OakBend Medical Center in Richmond.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
It's allergy season in Houston, and many are feeling its impact. But allergist Dr. Dat Tran said the pollen count is low compared to 2023.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Non-destructive testing techniques, such as dye penetrant testing, radiographic testing, and ultrasonic testing, play a vital role in identifying cracks in gearbox housings without causing damage to the component. These methods allow inspectors to detect internal defects or cracks that may not be visible to the naked eye, ensuring a thorough assessment of the housing's condition.
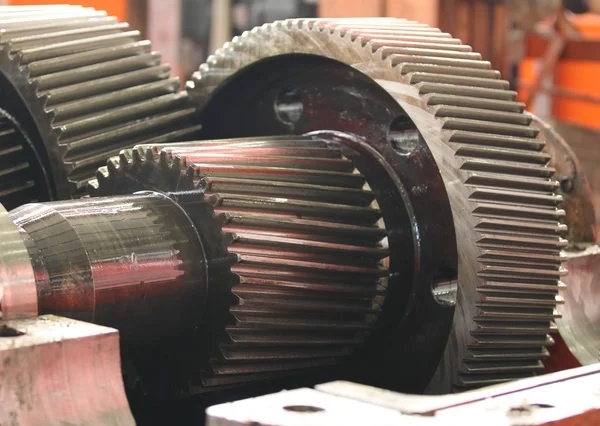

Certain types of cracks are more common in gearbox housings, such as fatigue cracks, stress cracks, and impact cracks. Fatigue cracks typically occur due to repeated loading and unloading of the gearbox, while stress cracks can result from excessive pressure or torque. Impact cracks, on the other hand, are caused by sudden impacts or collisions that can weaken the housing structure.
Expert Insights Into The Equipment Behind Industrial Gearbox Repair
Ultrasonic testing is a highly effective method for detecting cracks in gearbox housings by using high-frequency sound waves to penetrate the material and identify internal defects. This non-destructive technique can provide detailed information about the size, location, and severity of cracks, allowing for accurate assessment and timely repairs to prevent further damage.

Magnetic particle inspection is another valuable tool for detecting cracks in gearbox housings, particularly surface cracks that may not be visible to the naked eye. By applying a magnetic field and magnetic particles to the surface of the housing, inspectors can identify areas where magnetic particles are attracted, indicating the presence of cracks or defects that require attention.
Thermal imaging can be utilized to identify cracks in gearbox housings by detecting temperature variations that may indicate the presence of internal defects or cracks. By capturing infrared images of the housing, inspectors can identify areas of heat concentration or irregularities that may be caused by cracks, allowing for targeted inspections and maintenance to ensure the gearbox's reliability and safety.

In pharmaceutical applications, there are specific gearbox maintenance requirements that must be adhered to in order to ensure optimal performance and compliance with industry regulations. These requirements may include regular inspections, lubrication checks, and temperature monitoring to prevent contamination and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, proper documentation of maintenance activities and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are essential in pharmaceutical settings to guarantee the safety and efficacy of products. It is crucial for pharmaceutical companies to work closely with gearbox manufacturers and maintenance professionals to develop a comprehensive maintenance plan tailored to their specific needs and requirements. Failure to properly maintain gearboxes in pharmaceutical applications can result in costly downtime, product recalls, and potential regulatory issues.
Gearbox noise analysis can be a complex process that requires specialized techniques to accurately diagnose and address issues. Some of the key methods used in gearbox noise analysis include vibration analysis, acoustic testing, modal analysis, and frequency spectrum analysis. These techniques allow engineers to identify specific sources of noise within the gearbox, such as gear meshing, bearing defects, or lubrication issues. By using advanced tools such as accelerometers, microphones, and spectrum analyzers, experts can pinpoint the root cause of the noise and develop targeted solutions to reduce or eliminate it. Additionally, computer-aided design (CAD) software can be used to simulate gearbox operation and predict potential noise issues before they occur. Overall, a combination of these specialized techniques is essential for effective gearbox noise analysis and troubleshooting.
Indicators of gearbox shaft misalignment can include abnormal vibrations, increased noise levels, overheating, premature wear on bearings, and decreased efficiency in the transmission system. Other signs may include irregular gear tooth wear, shaft breakage, and coupling misalignment. These issues can lead to further damage to the gearbox components and result in costly repairs if not addressed promptly. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the gearbox shaft alignment are essential to prevent these problems and ensure optimal performance of the machinery.
To assess gearbox efficiency losses, engineers typically utilize a combination of methods such as performance testing, thermography, vibration analysis, and oil analysis. Performance testing involves measuring input and output power to calculate efficiency, while thermography can identify areas of overheating indicating energy loss. Vibration analysis helps detect mechanical issues that may be causing inefficiencies, and oil analysis can reveal contamination or wear particles that could be impacting performance. By combining these techniques, engineers can accurately assess gearbox efficiency losses and identify areas for improvement.
Preventing gearbox oil contamination from water can be achieved through various measures. One effective method is to ensure proper sealing of the gearbox to prevent water ingress. Regular maintenance and inspection of seals, gaskets, and O-rings can help identify any potential leaks that may allow water to enter the gearbox. Additionally, using high-quality gearbox oil with water-resistant properties can help mitigate the risk of contamination. Implementing a regular oil change schedule can also prevent water buildup in the gearbox. Furthermore, storing the gearbox in a dry and controlled environment can help minimize the chances of water contamination. Overall, a combination of preventive measures such as proper sealing, maintenance, oil selection, and storage practices can help safeguard the gearbox from water contamination.