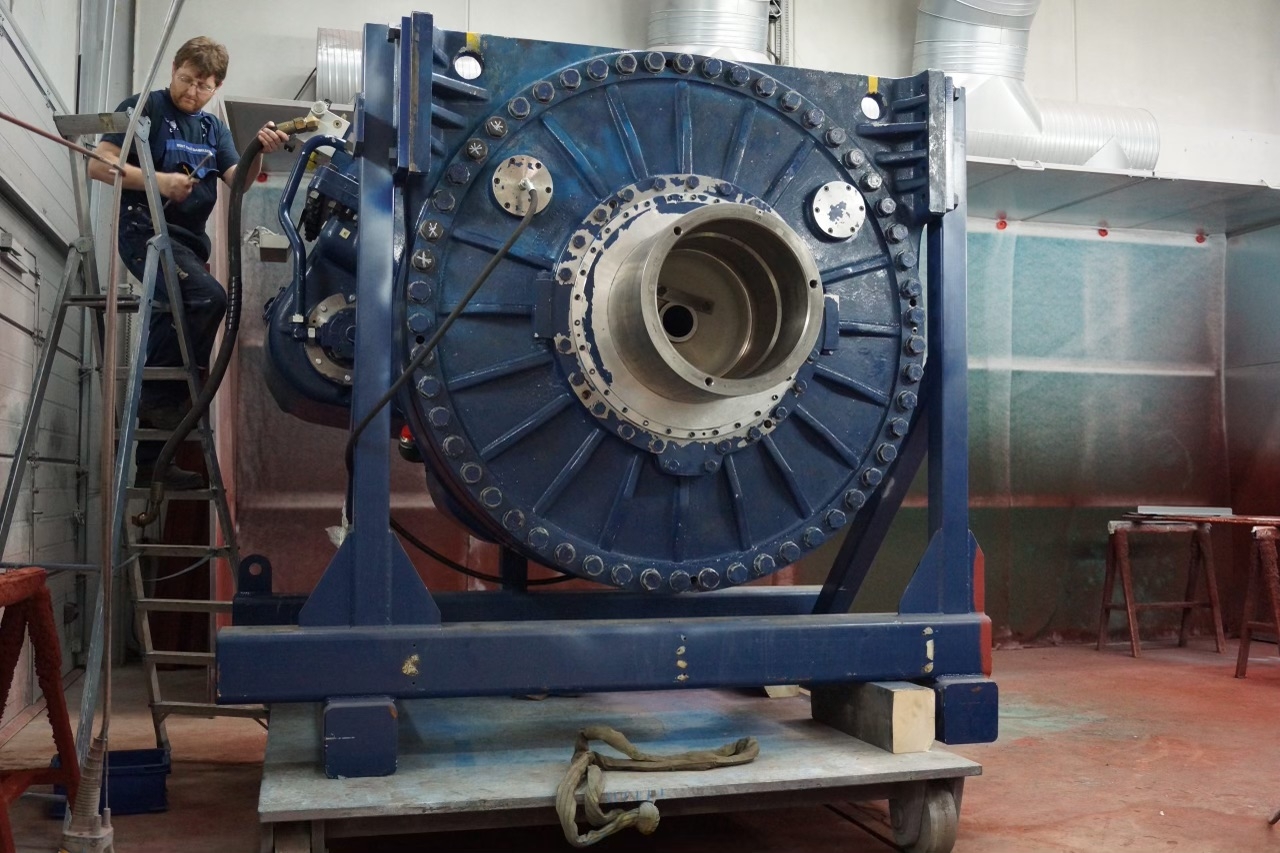


Gearbox components can fail due to various reasons, with common failure modes including gear tooth wear, bearing failure, shaft misalignment, and lubrication breakdown. Gear tooth wear can occur due to excessive loads, improper lubrication, or misalignment, leading to decreased efficiency and potential gear tooth breakage. Bearing failure can result from inadequate lubrication, contamination, or misalignment, causing increased friction, overheating, and ultimately component failure.
Expert Insights Into The Equipment Behind Industrial Gearbox Repair
Gear tooth wear and pitting can significantly impact gearbox performance by reducing the efficiency of power transmission and increasing noise levels. As gear teeth wear down or develop pits, the contact area between gears decreases, leading to higher stress concentrations and potential tooth breakage. This can result in decreased torque transmission, increased vibration, and ultimately, gearbox failure if not addressed promptly.
The cinema showed films for 64 continuous years, making it one of the longest-running theatres in the country.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
On Wednesday's show: We discuss the latest developments in politics, including whether runoffs ever have dramatically different results. Then we consider if we are ready for the next major public health emergency.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
Episode: 2998 Test Tube Evolution. Today, evolution in a test tube.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
Dr. Talat Jehan Khan, a pediatrician for Texas Children's Hospital, was stabbed to death Oct. 28 in an outdoor common area at Alys Luxury Living in Conroe. The man accused of killing her is jailed and faces a murder charge.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
The university is partnering with the Ibn Sina Foundation and the OakBend Medical Center in Richmond.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Lubrication breakdown in gearbox components can have detrimental effects on their performance and longevity. When lubrication breaks down, it can lead to increased friction between moving parts, causing overheating, wear, and premature failure. Inadequate lubrication can also result in corrosion, pitting, and increased noise levels, ultimately compromising the reliability and efficiency of the gearbox.
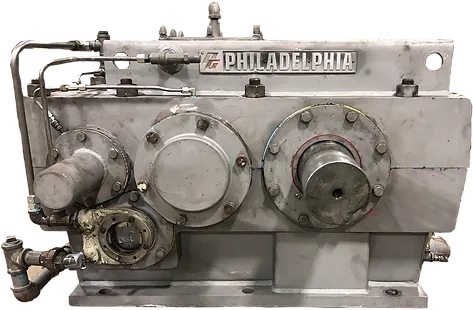
Misalignment in gearbox components can have a significant impact on their reliability and performance. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on bearings, gears, and shafts, causing premature wear, overheating, and ultimately, component failure. Proper alignment is crucial to ensure even distribution of loads and smooth operation of the gearbox, preventing unnecessary wear and reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Contamination plays a crucial role in causing gearbox component failures by introducing foreign particles into the system, leading to increased friction, wear, and corrosion. Contaminants such as dirt, dust, metal particles, and water can accelerate the breakdown of lubrication, damage gear teeth, and bearings, and compromise the overall performance of the gearbox. Regular maintenance and proper sealing are essential to prevent contamination and ensure the longevity of gearbox components.

Temperature fluctuations can contribute to gearbox component failures by causing thermal expansion and contraction, leading to misalignment, increased friction, and premature wear. Extreme temperature variations can affect the viscosity of lubricants, reducing their effectiveness in providing adequate protection to moving parts. Overheating can also accelerate the breakdown of lubrication, leading to increased wear and potential component failure if not addressed promptly.
Inadequate maintenance practices can have severe consequences on gearbox components, leading to increased wear, decreased efficiency, and ultimately, premature failure. Neglecting regular inspections, lubrication checks, and alignment adjustments can result in the accumulation of contaminants, improper lubrication, misalignment, and other issues that can compromise the reliability and performance of the gearbox. Proper maintenance practices are essential to ensure the longevity and optimal operation of gearbox components.
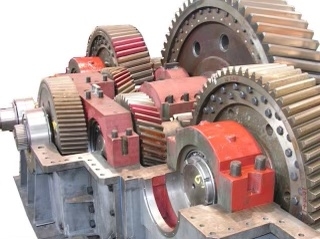
In order to reduce gearbox friction, various measures can be implemented. One approach is to use high-quality lubricants that have low viscosity and high thermal stability. Additionally, optimizing the gear tooth profile and surface finish can help minimize frictional losses. Utilizing advanced materials such as carbon fiber or ceramic coatings can also reduce friction within the gearbox. Proper alignment and clearance settings between gears can further decrease friction. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the gearbox components can ensure smooth operation and minimize friction over time. Overall, a combination of lubrication, design optimization, material selection, and maintenance practices can effectively reduce gearbox friction.
The performance of a gearbox can indeed be influenced by external factors such as temperature. Fluctuations in temperature can impact the viscosity of the lubricating oil within the gearbox, affecting its ability to properly lubricate the gears and bearings. Extreme temperatures can also cause thermal expansion or contraction of gearbox components, leading to misalignment or increased friction. Additionally, temperature variations can alter the material properties of gearbox components, potentially leading to premature wear or failure. Therefore, it is crucial for gearbox manufacturers to consider the effects of temperature on performance and design their products accordingly to ensure optimal operation in diverse environmental conditions.
Preventing gearbox corrosion in humid environments can be achieved by implementing various protective measures. One effective method is to apply a corrosion-resistant coating on the gearbox components, such as zinc plating or powder coating. Additionally, using desiccants or dehumidifiers in the surrounding area can help reduce moisture levels and prevent corrosion. Regularly inspecting the gearbox for any signs of corrosion and promptly addressing any issues can also help prevent further damage. Proper ventilation and ensuring proper drainage around the gearbox can also help mitigate the effects of humidity. Overall, a combination of protective coatings, moisture control, regular maintenance, and proper ventilation can help prevent gearbox corrosion in humid environments.
The maintenance schedule for gearbox seals should include regular inspections, typically every 6 months or as recommended by the manufacturer. During these inspections, it is important to check for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks in the seals. This can involve checking the seal material for cracks, tears, or deterioration, as well as ensuring proper alignment and tightness of the seals. Additionally, lubrication of the seals may be necessary to prevent friction and prolong their lifespan. Any issues found during inspections should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage to the gearbox and ensure optimal performance. Following a consistent maintenance schedule for gearbox seals can help prevent costly repairs and downtime in the long run.
Indicators of gearbox bearing wear can include symptoms such as increased noise levels, vibration, and difficulty shifting gears. Other signs may include leaks of gearbox oil, unusual smells coming from the transmission, and a decrease in overall performance. Additionally, visible damage to the bearings themselves, such as cracks or wear marks, can also indicate that they are in need of replacement. It is important to address gearbox bearing wear promptly to prevent further damage to the transmission system and ensure the vehicle operates safely and efficiently. Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify and address bearing wear before it leads to more serious issues.