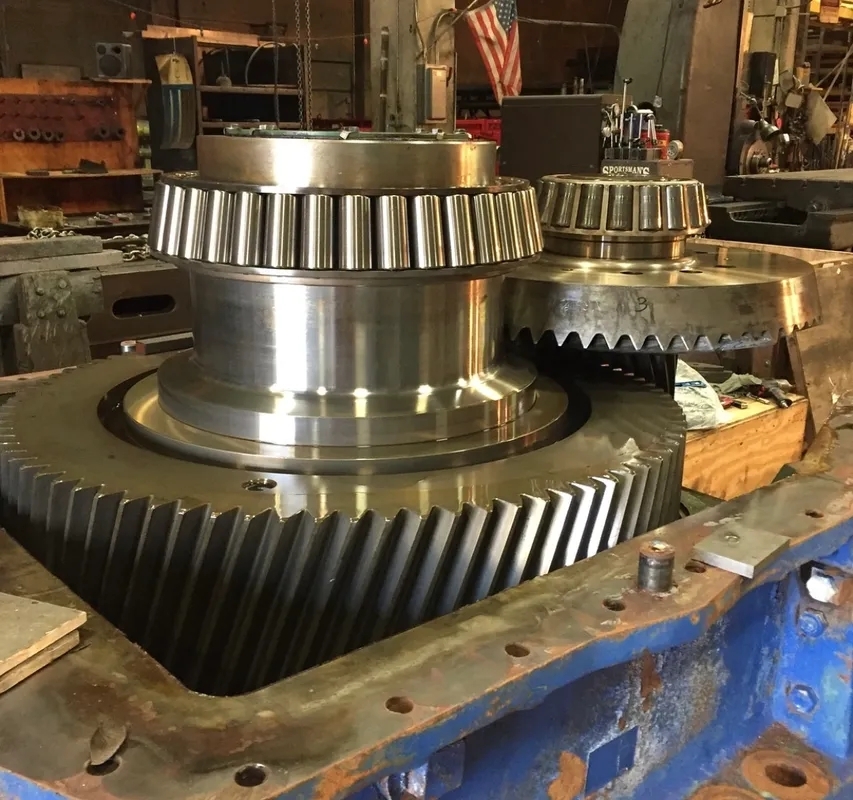


The common failure modes of gearboxes in industrial machinery include gear tooth wear, bearing failure, lubrication issues, and overheating. Gear tooth wear can occur due to misalignment, overload conditions, or inadequate lubrication, leading to decreased efficiency and potential breakdown. Bearing failure is often caused by misalignment, overloading, or lack of proper lubrication, resulting in increased friction and heat generation within the gearbox.
Lubrication plays a crucial role in impacting the failure modes of gearboxes. Proper lubrication helps reduce friction between moving parts, dissipates heat, and prevents wear and corrosion. Inadequate lubrication can lead to increased friction, overheating, and accelerated wear of gears and bearings, ultimately causing premature failure of the gearbox components.
Expert Insights Into The Equipment Behind Industrial Gearbox Repair
The cinema showed films for 64 continuous years, making it one of the longest-running theatres in the country.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
On Wednesday's show: We discuss the latest developments in politics, including whether runoffs ever have dramatically different results. Then we consider if we are ready for the next major public health emergency.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
Episode: 2998 Test Tube Evolution. Today, evolution in a test tube.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
Dr. Talat Jehan Khan, a pediatrician for Texas Children's Hospital, was stabbed to death Oct. 28 in an outdoor common area at Alys Luxury Living in Conroe. The man accused of killing her is jailed and faces a murder charge.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
The university is partnering with the Ibn Sina Foundation and the OakBend Medical Center in Richmond.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Misalignment is a significant factor in gearbox failure as it can result in uneven distribution of forces, increased wear on gear teeth and bearings, and decreased efficiency. Misalignment can occur due to improper installation, foundation issues, or external forces acting on the machinery. Addressing misalignment through proper alignment procedures can help prevent premature gearbox failure.

Overload conditions contribute to gearbox failure by subjecting the components to excessive stress and strain beyond their design limits. Overloading can lead to increased wear on gears and bearings, overheating, and ultimately, mechanical failure. Monitoring and controlling the load on the gearbox can help prevent damage and prolong the lifespan of the equipment.
Signs of impending gearbox failure that operators should look out for include unusual noises, vibrations, overheating, leaks, and changes in performance. Unusual noises such as grinding, whining, or knocking can indicate issues with gear teeth or bearings. Vibrations can signal misalignment or imbalance within the gearbox. Overheating can point to lubrication problems or overload conditions, while leaks may indicate seal or gasket failures.
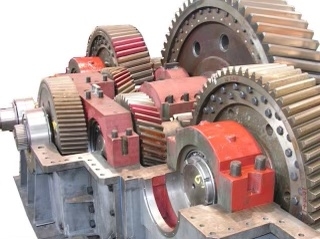
Regular maintenance and inspections are essential in preventing gearbox failure. Scheduled maintenance tasks such as lubrication checks, alignment adjustments, and vibration analysis can help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Inspections can also help detect wear, misalignment, or other issues early on, allowing for timely repairs and replacements to be made.
Ignoring gearbox failure warning signs can lead to catastrophic consequences, including unexpected downtime, costly repairs, production delays, and safety hazards. A gearbox failure can result in extensive damage to other machinery components, leading to increased repair costs and prolonged downtime. Regularly monitoring and addressing warning signs can help prevent these negative outcomes and ensure the continued operation of industrial machinery.
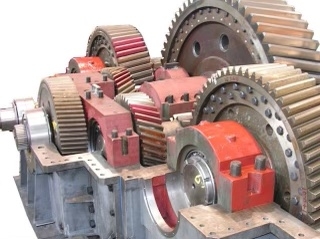
Gearbox temperature sensors play a crucial role in maintenance by monitoring the temperature of the gearbox to ensure optimal performance and prevent overheating. These sensors provide real-time data on the temperature of the gearbox, allowing maintenance technicians to identify any potential issues before they escalate. By detecting abnormal temperature fluctuations, these sensors help prevent damage to the gearbox components and extend the lifespan of the equipment. Additionally, gearbox temperature sensors can trigger alerts or shut down the system automatically if the temperature exceeds safe levels, preventing costly repairs and downtime. Regular monitoring and analysis of the data from these sensors are essential for proactive maintenance and ensuring the reliability of the gearbox.
One way to identify gearbox oil leaks is to look for visible signs of oil dripping or pooling underneath the vehicle. Other indicators may include a decrease in oil levels, a burning smell coming from the engine, or unusual noises while driving. Inspecting the gearbox for cracks, loose fittings, or damaged seals can also help pinpoint the source of the leak. Additionally, checking for oil residue on the transmission housing or surrounding components can provide clues as to where the leak is originating from. Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent gearbox oil leaks and ensure optimal performance of the vehicle.
Gearbox breathers play a crucial role in maintenance by preventing the buildup of pressure inside the gearbox, which can lead to leaks, seal failures, and other issues. These breathers allow for the release of excess air and gases that can accumulate during operation, helping to maintain optimal operating conditions and prolonging the lifespan of the gearbox components. By ensuring proper ventilation and preventing contamination from entering the gearbox, breathers help to reduce the risk of premature wear and damage, ultimately contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the system. Regular inspection and maintenance of gearbox breathers are essential to ensure they are functioning correctly and effectively protecting the gearbox from potential harm.
Assessing gearbox lubrication system performance involves monitoring various key indicators such as oil viscosity, temperature, pressure, and contamination levels. Regularly checking the oil level and quality, as well as inspecting for any leaks or unusual noises, can help determine the effectiveness of the lubrication system. Additionally, analyzing oil samples for wear particles and conducting vibration analysis can provide valuable insights into the overall health of the gearbox. Utilizing advanced technologies like online condition monitoring systems and thermal imaging can further enhance the assessment of gearbox lubrication system performance. By integrating these various monitoring techniques, maintenance professionals can ensure optimal lubrication system functionality and prevent potential equipment failures.