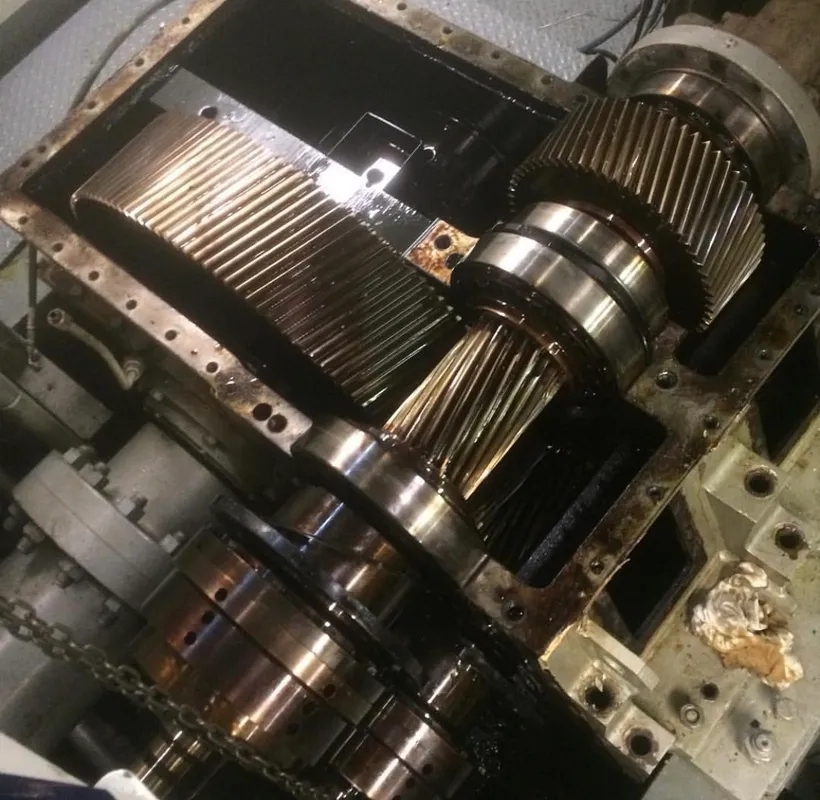

The gear ratio of a gearbox can be calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the driven gear by the number of teeth on the driving gear. This simple calculation provides a numerical representation of how many times the driven gear will rotate for each rotation of the driving gear.
The formula for determining the gear ratio in a gearbox is: Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Driven Gear / Number of Teeth on Driving Gear. By using this formula, one can easily calculate the gear ratio of a gearbox and understand the relationship between the driving and driven gears.
On Tuesday's show: We discuss a number of environmental stories across the state. And we consider how to deal with seasonal allergies as we near the official start of spring.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
Episode: 2851 The Lake Breeze Fan: Unplanned Obsolescence. Today, invention and obsolescence.
Posted by on 2024-03-12
The Livestock Show and Rodeo will continue through Sunday, March 17.
Posted by on 2024-03-11
The blooming cycle for Texas' state flower is 2-3 weeks ahead of schedule because of earlier-than-usual warm weather, according to Texas A&M horticulturalist Michael Arnold. Bluebonnets already can be seen in places such as the Houston Botanic Garden.
Posted by on 2024-03-11
The significance of gear ratio in a gearbox system lies in its ability to control the speed and torque of the output shaft. By adjusting the gear ratio, one can optimize the performance of the gearbox for specific applications, such as increasing speed for high-speed applications or increasing torque for heavy-duty tasks.

When selecting the gear ratio for a gearbox, factors such as the desired output speed, torque requirements, efficiency, and space constraints should be considered. It is important to choose a gear ratio that meets the specific needs of the application while also taking into account the limitations of the gearbox system.
Expert Insights Into The Equipment Behind Industrial Gearbox Repair
Different types of gearboxes may require different methods for calculating gear ratios, depending on the gear configuration and design. For example, some gearboxes may use planetary gears or helical gears, which may require different formulas or calculations to determine the gear ratio accurately.
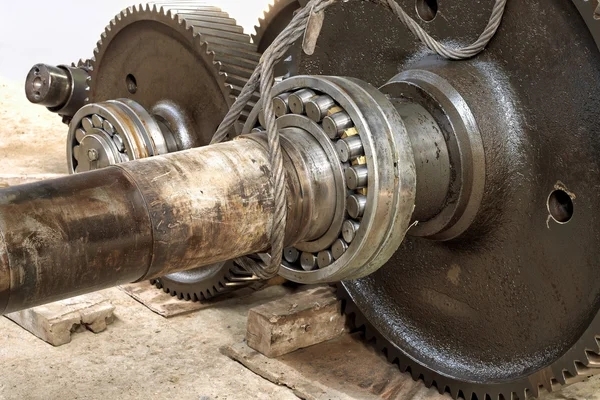

The number of teeth on the gears directly affects the gear ratio in a gearbox. A gear with more teeth will result in a higher gear ratio, providing more torque but lower speed, while a gear with fewer teeth will result in a lower gear ratio, offering higher speed but lower torque. The number of teeth on the gears plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance of the gearbox.
The pitch diameter of the gears is essential in determining the gear ratio of a gearbox. The pitch diameter is the effective diameter of the gear where the teeth mesh, and it directly influences the gear ratio calculation. By considering the pitch diameter along with the number of teeth on the gears, one can accurately determine the gear ratio of a gearbox and optimize its performance for specific applications.

Detecting gearbox oil oxidation can be done by monitoring the oil's color, viscosity, and odor. Oxidized gearbox oil may appear darker in color, have a thicker consistency, and emit a burnt or acrid smell. Additionally, testing the oil for acidity levels can also indicate oxidation. Other signs of gearbox oil oxidation include increased levels of sludge or varnish in the oil, decreased lubricating properties, and potential damage to the gearbox components. Regular oil analysis and maintenance can help prevent and detect gearbox oil oxidation before it causes significant damage to the system.
When troubleshooting gearbox clutch problems, it is important to first check for any signs of slipping, grinding, or difficulty shifting gears. Inspecting the clutch pedal for any unusual resistance or play can also provide valuable information. Additionally, examining the clutch fluid levels, clutch master cylinder, and clutch release bearing can help pinpoint the issue. Testing the clutch engagement and disengagement, as well as checking for any leaks or damage to the clutch components, can further aid in diagnosing the problem. It is recommended to consult a professional mechanic for a thorough inspection and proper diagnosis of gearbox clutch issues.
Gearbox lubrication failure can have severe consequences on the overall performance and longevity of a vehicle's transmission system. Without proper lubrication, the gears within the gearbox can experience increased friction, leading to excessive wear and tear. This can result in overheating, increased noise levels, and ultimately, mechanical failure. Additionally, inadequate lubrication can cause the gears to seize up or become misaligned, further compromising the functionality of the gearbox. In the long run, gearbox lubrication failure can lead to costly repairs or even the need for a full transmission replacement. Regular maintenance and monitoring of gearbox lubrication levels are essential to prevent these detrimental outcomes.
When troubleshooting gearbox cooling system problems, it is important to first check for any leaks in the system, such as from the transmission cooler or lines. Inspecting the radiator for any blockages or damage is also crucial. Additionally, checking the condition of the transmission fluid and ensuring it is at the correct level can help identify any issues. Testing the functionality of the thermostat, fan, and other cooling components can provide insight into potential malfunctions. It is recommended to consult the vehicle's manual for specific troubleshooting steps and to consider seeking professional assistance if needed. Regular maintenance and inspection of the gearbox cooling system can help prevent problems from occurring in the future.
The performance of a gearbox can indeed be affected by changes in altitude. Altitude variations can impact the air density, which in turn affects the cooling efficiency of the gearbox. Additionally, altitude changes can alter the pressure levels, potentially leading to issues with lubrication and overall gearbox functionality. It is important for gearbox manufacturers to consider these factors and design their products to withstand different altitude conditions to ensure optimal performance in various environments. Proper maintenance and adjustments may be necessary to account for altitude changes and prevent any negative effects on gearbox performance.
The efficiency of a gearbox can indeed be affected by changes in altitude. As altitude increases, the air becomes less dense, which can impact the performance of the gearbox. This is particularly true for gearboxes in vehicles or machinery that rely on air for cooling, as the reduced air density at higher altitudes can lead to decreased cooling efficiency. Additionally, changes in altitude can also affect the lubrication of the gearbox, as lower air pressure can result in reduced oil flow and lubrication effectiveness. Therefore, it is important for manufacturers to consider altitude variations when designing gearboxes to ensure optimal performance across different environments.