

Gear load testing in the automotive industry serves the purpose of evaluating the performance and durability of gears under various load conditions. By subjecting gears to different levels of stress and measuring their response, manufacturers can ensure that the gears meet the required standards for quality and reliability.
Gear load testing plays a crucial role in ensuring the durability and reliability of gearboxes in heavy machinery by simulating real-world operating conditions. By applying specific loads and monitoring the gearbox's performance, engineers can identify potential weaknesses or design flaws that could lead to premature failure. This testing helps manufacturers optimize the gearbox design to withstand the harsh conditions of heavy machinery operation.
Expert Insights Into The Equipment Behind Industrial Gearbox Repair
Roxanna Asgarian discusses her book on the tragedy of the Hart family and their adopted children.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
In Texas and across the country, young people and their families have become increasingly skeptical of the benefits of college. Negative public perception of higher education costs has mostly centered around four-year, private institutions. Experts say community colleges often get lumped into that conversation, even though they usually have lower tuition rates.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
Chief Daniel Rodriguez was taking pre-scheduled vacation time in Phoenix during the Robb Elementary School shooting on May 24, 2022.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
The event will host 20 mile, 40 mile and 60 mile races around the metropolitan, but a map hasn't yet been released. Beginning and ending at Avenida de las Americas at Discovery Green, check-in and registration for the event begins at 6:30 a.m. The routes are secured until 1 p.m., and riders can hop on the sag wagon to continue the ride without support after that, according to the event's webpage.
Posted by on 2024-03-13
Different methods are used for simulating real-world load conditions during gearbox testing, including static load testing, dynamic load testing, and endurance testing. Static load testing involves applying a constant load to the gearbox to measure its response, while dynamic load testing simulates varying loads to assess the gearbox's performance under different conditions. Endurance testing involves subjecting the gearbox to continuous operation at high loads to evaluate its long-term durability.
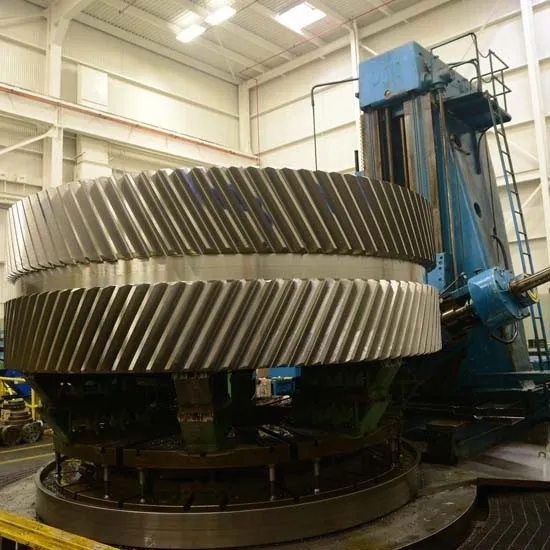

Manufacturers determine the maximum load capacity of a gearbox through load testing by gradually increasing the applied load until the gearbox reaches its breaking point. By measuring the gearbox's response to increasing loads, engineers can establish the maximum load that the gearbox can withstand without failure. This information is crucial for setting safety margins and ensuring the gearbox's reliability in real-world applications.
Computer simulation plays a significant role in optimizing gear load testing processes by allowing engineers to model and analyze the gearbox's behavior under different load conditions. By using advanced software tools, manufacturers can simulate various scenarios, predict potential failure points, and optimize the gearbox design before conducting physical load testing. This helps streamline the testing process and improve the overall efficiency of gearbox development.
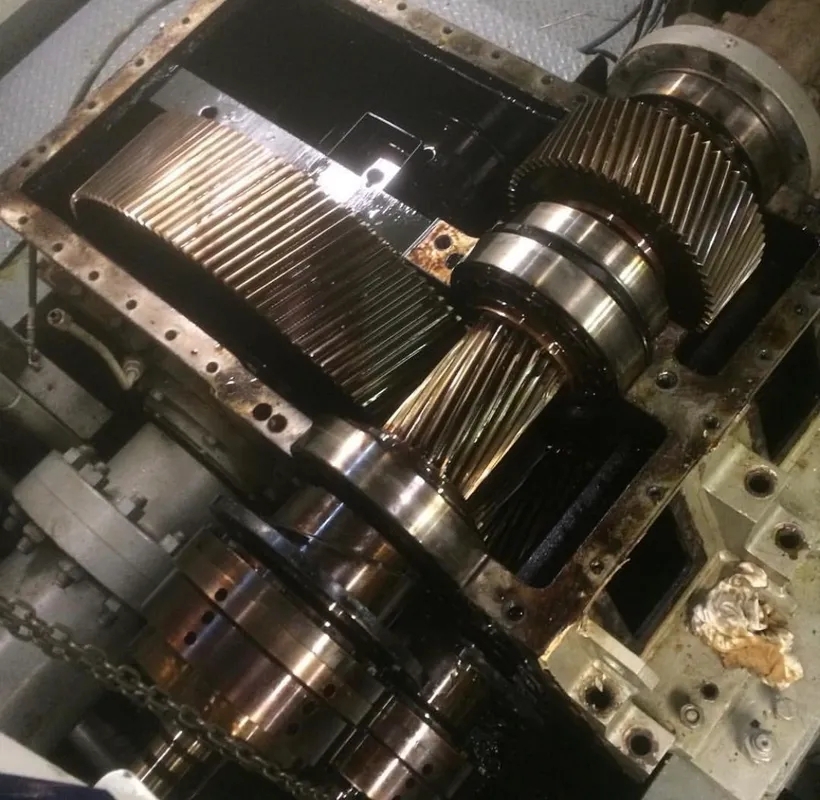
Gear load testing standards such as ISO 6336 contribute to ensuring quality control in gearbox manufacturing by providing guidelines for testing procedures and performance criteria. These standards help manufacturers establish consistent testing protocols, compare results across different products, and ensure that gearboxes meet the required quality and reliability standards. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers build trust with customers and maintain a high level of quality in their products.
During gear load testing, engineers monitor key parameters such as torque, speed, temperature, vibration, and noise levels to assess the gearbox's performance and identify potential issues. By analyzing these parameters during testing, engineers can detect abnormalities, predict potential failures, and make necessary adjustments to improve the gearbox's reliability and durability. Monitoring these parameters throughout the testing process is essential for ensuring the gearbox meets the required performance standards.
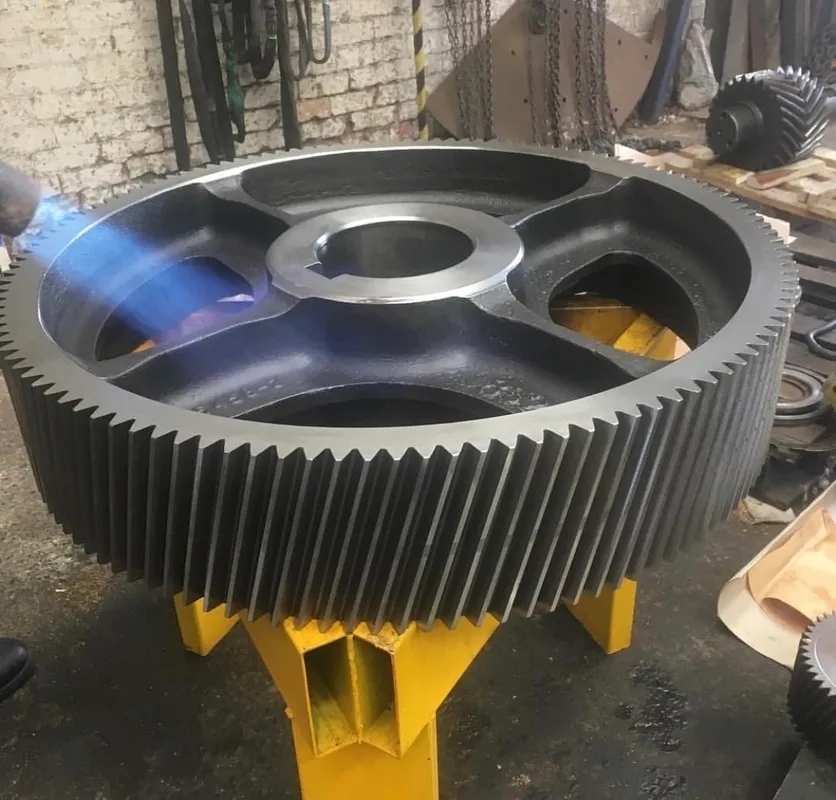

The efficiency of a gearbox can indeed be affected by the gearbox gear ratio. The gear ratio in a gearbox refers to the relationship between the number of teeth on the input gear to the number of teeth on the output gear. A higher gear ratio means that the output gear will rotate more times for every rotation of the input gear. This can impact the efficiency of the gearbox as higher gear ratios can lead to increased friction and energy losses due to the increased number of gear engagements. Conversely, lower gear ratios can improve efficiency by reducing the number of gear engagements and minimizing energy losses. Therefore, selecting the appropriate gear ratio is crucial in optimizing the efficiency of a gearbox.
To prevent gearbox oil oxidation, several measures can be taken. One effective method is to use high-quality synthetic oils that contain antioxidants and anti-oxidation additives. Regularly changing the gearbox oil at recommended intervals can also help prevent oxidation. Keeping the gearbox properly sealed and protected from moisture and contaminants can further reduce the risk of oxidation. Additionally, maintaining proper operating temperatures and avoiding excessive heat can help prolong the life of the gearbox oil and prevent oxidation. Monitoring the oil condition regularly through oil analysis can also help detect early signs of oxidation and take corrective actions. Overall, a combination of using high-quality oils, regular maintenance, proper sealing, and monitoring can help prevent gearbox oil oxidation.
Gearbox breather vents play a crucial role in maintenance by allowing for the release of excess pressure and preventing the buildup of moisture and contaminants within the gearbox. These vents help to regulate the internal temperature of the gearbox, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the components. By allowing for the escape of gases and preventing the ingress of debris, breather vents help to maintain the proper lubrication and functionality of the gearbox. Regular inspection and maintenance of these vents are essential to prevent issues such as overheating, corrosion, and premature wear of gearbox components. Proper care of gearbox breather vents can extend the lifespan of the gearbox and reduce the likelihood of costly repairs.
The key components of a gearbox lubrication system include a reservoir or oil pan to store the lubricant, a pump to circulate the oil throughout the gearbox, a filter to remove any contaminants from the oil, and a series of channels or passages to distribute the oil to the various components of the gearbox. Additionally, there may be sensors to monitor the oil level and temperature, as well as valves to control the flow of oil. Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing wear and tear on the gearbox components, ultimately extending the lifespan of the system. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the lubrication system are crucial to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
In marine applications, specialized gearbox maintenance procedures are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. These procedures typically involve regular inspections, lubrication checks, and alignment adjustments to prevent wear and tear caused by harsh marine environments. Specific tasks may include checking oil levels, monitoring for water contamination, inspecting seals and gaskets, and replacing worn components as needed. Additionally, marine gearbox maintenance may also involve monitoring vibration levels, conducting oil analysis, and following manufacturer recommendations for service intervals. By following these specialized procedures, marine operators can minimize downtime, reduce the risk of costly repairs, and prolong the lifespan of their gearboxes.
To assess gearbox wear and tear, one can start by inspecting the gears, bearings, shafts, and seals for any signs of damage such as pitting, scoring, or corrosion. It is also important to check for any abnormal noises, vibrations, or leaks coming from the gearbox. Additionally, measuring the backlash, runout, and gear tooth wear can provide valuable information about the condition of the gearbox. Performing oil analysis can help determine if there are any metal particles or contaminants present in the lubricant, indicating potential wear. Regular maintenance and monitoring of these factors can help prevent further damage and ensure the gearbox operates efficiently.